Tarsal tunnel Syndrome
The tarsal tunnel is located on the inside of the ankle, and is formed by the ankle bones and the band of ligaments that stretches across the
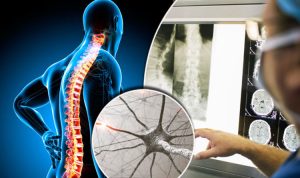
What is Motor Neuron Disease?
The motor neuron diseases (MNDs) are a group of progressive neurological disorders that destroy cells that control essential muscle activity such as speaking, walking, breathing, and swallowing. Normally, messages from nerve cells in the brain (called upper motor neurons) are transmitted to nerve cells in the brain stem and spinal cord (called lower motor neurons) and from them to particular muscles. When there are disruptions in these signals, the result can be gradual muscle weakening, wasting away, and uncontrollable twitching (called fasciculation’s). Eventually, the ability to control voluntary movement can be lost. MNDs may be inherited or acquired, and they occur in all age groups. MNDs occur more commonly in men than in women, and symptoms may appear after age 40. In children, particularly in inherited or familial forms of the disease, symptoms can be present at birth or appear before the child learns to walk.

Types of Motor Neuron Disease?
The main types of MND are:
What are the symptoms of MND?
MND is a progressive disease that usually starts slowly and gets worse over time. Symptoms sometimes starting on one side of the body and then spreading. Usually, the first things people notice are:
Later on, people with MND:
A few people with MND develop a type of dementia.
If you have MND, your sense of sight, touch, smell, hearing and taste won’t be affected.
What causes MND?
The exact cause of MND is not known. You can’t catch MND from somebody.
Generally, MND is believed to be caused because of a combination of environmental, lifestyle and genetic factors.
Most cases of MND occur spontaneously without any identifiable cause. Around 1 in 10 cases are ‘familial’ (meaning the condition is inherited) due to a genetic mutation (or error in the gene).
If a person has an MND-related genetic mutation, their children have a 50/50 chance of inheriting the MND-related genetic mutation.
If a person in your family has MND, other people in the family can be tested to see if they have the genetic mutation.
People who inherit the genetic mutation have a high chance of developing MND, but not all people with the genetic mutation will develop MND.
How is MND diagnosed?
MND can be hard to diagnose when the symptoms first appear because it seems like a lot of other conditions at first.
You may have a range of tests, some which eliminate other conditions.
Your doctor may refer you to a neurologist who will examine you and do various tests. These may include:
Although there is no cure for ALS-MND, treatments can help both to slow the disease and also to improve any symptoms you may have.
In this treatment, you are given a mask ventilator system to wear overnight while you are sleeping. The machines are small and portable and you can choose from a variety of different masks to suit you. People using this have been shown not only to have longer survival but also an improvement in the quality of their lives.
Treatments are available for many of the symptoms that you may develop with ALS-MND. These may include cramps, difficulty swallowing saliva and food, urinary symptoms and depression.
It can be fairly common for people with ALS-MND to have feeding problems. These may either be due to difficulty swallowing or to difficulty in actually feeding yourself due to the weakness in your arms and hands. Some people find that having thickened fluid and sitting very upright when eating are beneficial.
If you are losing weight as a result of having feeding difficulties then you may benefit from having a gastrostomy inserted. This is a small feeding tube that is placed through the wall of the tummy (abdomen) directly into your stomach. Your doctor will discuss this in more detail with you if this might be appropriate for you.
Most people with ALS-MND are cared for by a professional team which includes neurologists, specialist nurses, physiotherapists, speech and language therapists, occupational therapists, dieticians and counsellors. Each problem that arises is assessed and dealt with as far as possible by the relevant members of the team.
MND does shorten life expectancy, and is a fatal illness. However, there is huge variation in how quickly it progresses, and it is different in each person who has it. Muscles weakened by ALS-MND do not recover. However, weeks or months may go by where the disease does not seem to progress. Eventually, severe disability develops. As the disease becomes severe, people with ALS-MND are unable to walk, talk or eat, and need a lot of care.
Your specialist may be able to give you an idea of how quickly MND is likely to progress in your particular case. However, the outlook (prognosis) for people with ALS-MND is extremely variable:
In the other, rarer types of MND, progress may be slower and the outlook better.
There are many research studies looking at different potential treatments for ALS-MND. It is hoped that new treatments will be introduced in the future.
The tarsal tunnel is located on the inside of the ankle, and is formed by the ankle bones and the band of ligaments that stretches across the
Morton’s neuroma is a thickening of the tissue that surrounds the small nerve leading to the toes. It occurs as the nerve passes under the
What is Motor Neuron Disease? The motor neuron diseases (MNDs) are a group of progressive neurological disorders that destroy cells that control essential muscle activity
Whiplash is a neck injury caused by sudden movement of head. It is commonly happened during car driving because of rear-end car accidents. But whiplash can also
The thoracic outlet is basically a small area, the space between your collarbone and your first rib & vertebrae. Thoracic outlet syndrome is a group
Pelvic Floor The pelvic floor is made up of several muscles, ligaments and tissues that surround the pelvic bone and support that rectum like a
